Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just a technological advancement but a transformative force reshaping industries, businesses, and the job market. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on employment is becoming increasingly significant, presenting both opportunities and challenges for workers, businesses, and policymakers. In this comprehensive article, we will explore how AI is shaping the job market, the opportunities it creates, the challenges it poses, and strategies for navigating this new era of work.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence, once confined to science fiction, is now a pervasive part of our daily lives. From voice assistants and recommendation systems to autonomous vehicles and advanced data analytics, AI technologies are revolutionizing industries across the globe. One of the most profound impacts of AI is its effect on the job market. As AI capabilities expand, they are automating tasks traditionally performed by humans, creating new job roles, and fundamentally changing the nature of work.
Understanding the impact of AI on employment is crucial for individuals planning their careers, businesses strategizing their operations, and policymakers shaping economic policies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the opportunities and challenges brought about by AI in the job market, offering insights into how stakeholders can adapt and thrive in an AI-driven economy.
Opportunities Created by AI
1. Emergence of New Job Roles
AI is not just replacing jobs but also creating new ones. The advancement of AI technologies has led to the emergence of specialized job roles that require skills in AI development, data analysis, and machine learning. Some of the key new job roles include:
- AI Specialists and Engineers: Professionals who develop AI algorithms, build machine learning models, and integrate AI solutions into various applications.
- Data Scientists and Analysts: Experts who analyze large datasets, derive insights, and make data-driven decisions using AI and machine learning techniques.
- AI Ethicists and Policy Analysts: Individuals who address ethical considerations related to AI development and implementation, ensuring responsible and fair use of AI technologies.
- Robotics Engineers: Engineers specializing in designing, programming, and maintaining AI-powered robots and autonomous systems.
These new job roles not only require technical expertise but also creativity, problem-solving skills, and the ability to adapt to rapidly evolving technology.
2. Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
AI has the potential to significantly enhance productivity and efficiency across industries. By automating routine and repetitive tasks, AI allows workers to focus on more complex and strategic activities. For example:
- Manufacturing: AI-powered robots and automation systems streamline production processes, reduce errors, and increase output. Predictive maintenance powered by AI helps prevent equipment breakdowns, minimizing downtime and optimizing production schedules.
- Healthcare: AI applications in healthcare, such as medical image analysis, personalized treatment recommendations, and virtual health assistants, improve diagnosis accuracy, patient outcomes, and operational efficiency.
- Finance: AI-driven algorithms analyze financial data in real-time, detect fraudulent activities, and optimize investment portfolios. This automation improves decision-making processes and reduces operational costs.
By augmenting human capabilities with AI, businesses can achieve higher levels of efficiency and innovation, driving economic growth and competitiveness.
3. Upskilling and Reskilling Opportunities
As AI transforms industries and job roles, there is a growing demand for workers with skills in AI development, data science, and digital literacy. Upskilling and reskilling programs play a crucial role in preparing the workforce for the jobs of the future. Key areas for skills development include:
- Data Science and Machine Learning: Training in data analysis, machine learning algorithms, and AI model development equips professionals with the skills to leverage AI technologies effectively.
- Cybersecurity: With the increasing reliance on AI-powered systems, cybersecurity skills are essential to protect data, systems, and networks from cyber threats and breaches.
- AI Literacy: Basic knowledge of AI concepts and applications is becoming essential across various industries, enabling workers to collaborate with AI systems and make informed decisions.
Governments, educational institutions, and businesses are investing in training programs to ensure that workers are equipped with the skills needed to succeed in an AI-driven economy. These initiatives aim to bridge the skills gap, promote lifelong learning, and foster a workforce that can thrive amidst technological advancements.
Challenges Posed by AI
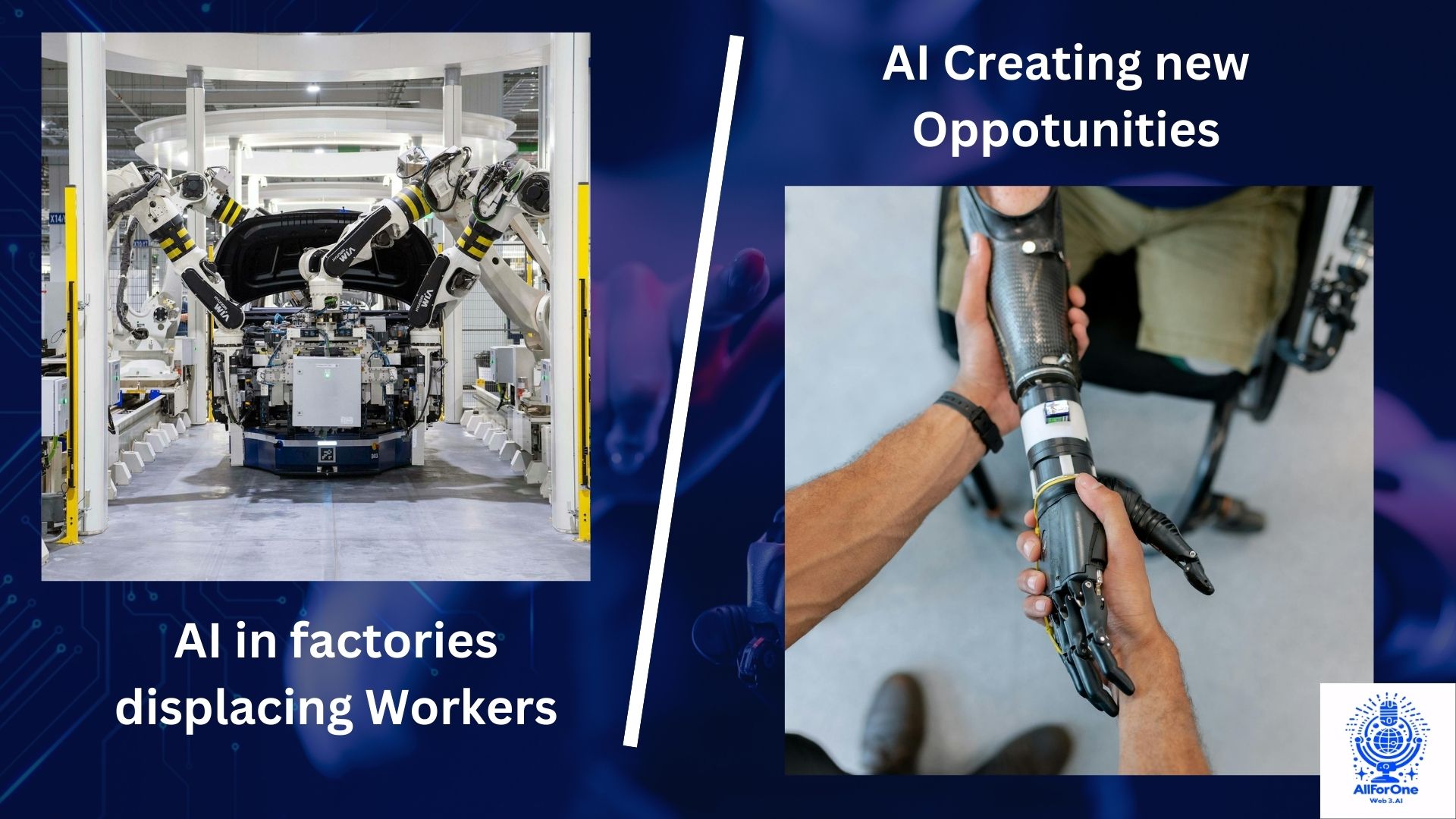
1. Job Displacement and Automation
While AI creates new opportunities, it also poses challenges, particularly in terms of job displacement and automation. Automation technologies powered by AI have the potential to replace human workers in routine, repetitive, and predictable tasks. Industries most susceptible to job displacement include:
- Manufacturing: AI-powered robots and automated assembly lines can perform manufacturing tasks more efficiently and accurately than human workers.
- Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries, process orders, and provide support, reducing the need for human customer service representatives.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and AI-powered logistics systems have the potential to automate driving and transportation services, impacting jobs in the transportation and logistics sectors.
Job displacement due to AI automation raises concerns about unemployment, economic inequality, and the need for workforce transitions. Addressing these challenges requires proactive strategies to support displaced workers, promote job creation in emerging industries, and foster inclusive economic growth.
2. The Digital Divide and Inequality
The rapid adoption of AI technologies has highlighted disparities in access to education, training, and employment opportunities. The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals and communities that have access to digital technologies and those that do not. In the context of AI, the digital divide manifests as unequal access to AI education, skills development programs, and high-tech job opportunities.
To bridge the digital divide and promote inclusive growth, stakeholders must:
- Expand Access to Education: Increase funding and resources for AI education and training programs in schools, universities, and vocational institutions.
- Promote Diversity in AI: Encourage diversity and inclusion in AI development teams to mitigate bias and ensure that AI technologies serve diverse populations equitably.
- Support Lifelong Learning: Establish policies and initiatives that promote lifelong learning and skills development to empower individuals to adapt to technological advancements.
By addressing the digital divide, policymakers and organizations can create a more inclusive and equitable society where all individuals have the opportunity to benefit from AI technologies and contribute to economic prosperity.
3. Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Frameworks
As AI technologies become more integrated into society, they raise ethical considerations regarding privacy, bias, accountability, and transparency. Ensuring responsible AI development and deployment requires robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Key considerations include:
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms may inadvertently reflect biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Mitigating algorithmic bias requires diverse and representative datasets, algorithmic transparency, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
- Privacy and Data Protection: AI systems often rely on large volumes of data, raising concerns about data privacy, security, and consent. Strong data protection laws, encryption technologies, and privacy-enhancing technologies are essential to safeguard personal and sensitive information.
- Accountability and Transparency: Establishing clear accountability mechanisms and transparency requirements for AI developers and users promotes trust and confidence in AI technologies. Organizations should disclose how AI systems make decisions and provide mechanisms for recourse in case of errors or misuse.
Governments, regulatory bodies, and industry stakeholders play a critical role in developing and enforcing ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks that ensure AI technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
Case Studies
1. AI Creating Job Opportunities: The Case of Microsoft

Microsoft is a leading example of how AI can create job opportunities and drive economic growth. The company has invested heavily in AI research and development, focusing on innovative solutions in areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability. Microsoft’s AI for Good initiative aims to harness AI technologies to address global challenges and create positive social impact. By collaborating with academic institutions, nonprofits, and government agencies, Microsoft has created thousands of new job roles in AI engineering, data science, and project management.
2. AI-Induced Job Displacement: The Case of Retail Automation
Retail automation provides a compelling example of how AI technologies can lead to job displacement. Companies like Amazon have implemented AI-powered robots and automated systems in their warehouses and fulfillment centers to streamline operations and improve efficiency. While automation has enabled faster order processing and delivery times, it has also reduced the demand for human labor in tasks such as picking, packing, and inventory management. To address the impact of automation on jobs, Amazon has launched upskilling programs and career development initiatives to help displaced workers transition to new roles within the company.
Future Outlook

Predictions for the Next Decade
Looking ahead, the future of work in an AI-driven economy is expected to undergo significant transformations. Some key predictions include:
- Increased Automation: AI technologies will continue to automate routine tasks across industries, reshaping job roles and workforce dynamics.
- Rise of Gig Economy Platforms: AI-powered platforms and digital marketplaces will facilitate freelance and gig work, offering flexibility and new earning opportunities for workers.
- Demand for AI Skills: The demand for professionals with AI skills, such as data science, machine learning, and AI ethics, will continue to grow as organizations prioritize digital transformation and innovation.
- Focus on Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaboration between humans and AI systems will become increasingly important, with AI augmenting human capabilities in decision-making, problem-solving, and creativity.
The Role of Governments and Educational Institutions
Governments, educational institutions, and businesses play a crucial role in preparing the workforce for the AI-driven future. Key actions include:
- Investment in Education and Training: Increase funding for AI education and skills development programs to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills needed for high-demand job roles.
- Promotion of Digital Inclusion: Expand access to broadband internet and digital technologies to bridge the digital divide and ensure equal opportunities for all.
- **Development of Ethical Guidelines and Regulatory Frameworks**: Collaborate with industry stakeholders to establish ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks that govern the responsible use of AI technologies.
- Support for Research and Innovation: Invest in AI research and innovation to drive technological advancements and promote economic growth and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI is a transformative force that is reshaping the job market, presenting both opportunities and challenges for individuals, businesses, and societies. While AI has the potential to create new job roles, enhance productivity, and improve quality of life, it also raises concerns about job displacement, economic inequality, and ethical implications. By investing in education, skills development, and ethical governance, stakeholders can harness the full potential of AI while mitigating its negative impacts.
As we navigate the complexities of an AI-driven economy, it is essential to adopt a proactive and inclusive approach to ensure that AI technologies benefit everyone. By fostering innovation, promoting digital inclusion, and upholding ethical standards, we can build a future where AI enhances human potential, drives economic prosperity, and creates a more equitable society.